The Diazyme Enzymatic Homocysteine (Hcy) Assay reagent is a liquid stable system, which provides a fast, accurate cost effective alternative to cumbersome and expensive immunochemical methods. Accurate and reliable, the assay features excellent correlation with HPLC and Immunochemical methods with a linear range of 3-50 μmole/L and intra and inter %CV values of < 5.9%.
| Product | Catalog Number | Format |
|---|---|---|
| Kit | DZ568A |
R1: 1 x 25.5 mL |
| Calibrator | DZ568A-CA5 | Cal: 5 x 3 mL vial |
| Control | DZ568A-CON | Con: 4 x 3 mL vial |
The Diazyme Enzymatic Homocysteine (Hcy) Assay reagent is a liquid stable system, which provides a fast, accurate cost effective alternative to cumbersome and expensive immunochemical methods. Accurate and reliable, the assay features excellent correlation with HPLC and Immunochemical methods with a linear range of 3-50 μmole/L and intra and inter %CV values of < 5.9%. The assay has no significant interference from lipemic and hemolytic substances and eliminates the "carry-over" interference with iron or lipase reagents that can occur with other methods. More significantly, the assay is not interfered by the endogenous cystathionine and therefore can be used with confidence in patients with renal disease.
Assay Principle
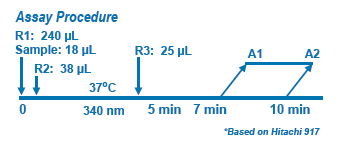
The Diazyme Hcy Enzymatic Assay is based on a novel assay principle that assesses the co-substrate conversion product. In the assay, oxidized Hcy is first reduced to free Hcy which then reacts with a co-substrate, SAM, catalyzed by a homocysteine S-methyltransferase. The co-substrate conversion product is amplified by coupled enzymatic cycling reactions. The tHcy level in the sample is directly proportional to the amount of NADH conversion to NAD+ (ΔA 340nm).
Intended use
The Diazyme Homocysteine Enzymatic Assay kit is intended for the in vitro quantitative determination of total L-homocysteine in serum or plasma. The assay can assist in diagnosis and treatment of patients suspected of having hyperhomocysteinemia and homocystinuria.
Patients who are taking methotrexate, carbamazepine, phenytoin, nitrous oxide, anticonvulsants, or 6-azuridine triacetate may have higher levels of Hcy due to metabolic interference with Hcy metabolism.
Regulatory Status

 Health Canada Registered
Health Canada Registered

